News in brief
Knowledge and description of sedimentary systems
Sedimentary budgets: concept, methods and integration in basin analysis on a land-sea continuum In a given sediment compartment , the sedimentary budget consists in evaluating sedimentary inputs, transfers and exports, and equating them to the net gain or loss over a specified period of time Sedimentary budgets are very widely used in geosciences. when integrated on a larger scale, they offer the possibility of acquiring a global vision of sedimentary systems.

News in brief
Organic matter characterization
Analytical methodologies for the characterization of organic matter : Application to the characterization of complex reservoir source rocks, oils, lubricants, polymers, microplastics, corrosion inhibitors and solid deposits present in geothermal energy facilities

News in brief
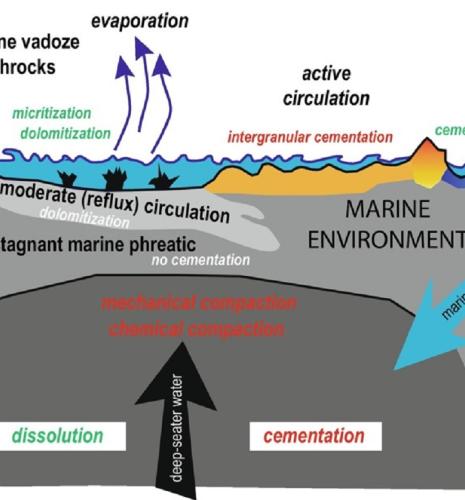
Natural gas in marine sediments: a climate issue?
Just like carbon dioxide (CO2), but with a much higher GWPa, methane CH4) is a gas which, according to the IEAb, is responsible for around 30% of the increase in global temperatures since the industrial revolution...

News in brief
The unlikely ellipticity of eigen modes of propagation of transmitted seismic body waves in homogeneous viscoelastic anisotropic media.
The hypothesis of elliptical particle motion of eigen body S-waves projected on a supposed common plane of elliptical polarization of any one of the eigen S-wave vectors S1, S2 associated to a given
Individual page
Julien COATLÉVEN
Research engineer in scientific computing
Julien Coatléven graduated from ENSTA (Paris) and completed his doctoral thesis in Applied Mathematics at Ecole Polytechnique (Paris) and INRIA Rocquencourt. After completing post-doctoral research at

News in brief
Colloid transport in porous media: deposits and plugging
The transport of colloidal particles in porous media is relevant to a number of fields, including geosciences and environmental engineering. Particle-matrix interactions can lead to deposit formation and accumulation, potentially damaging the medium and altering its permeability. (...) At IFPEN, the problem was originally studied for oil and gas production, but research has now been extended to include the fields of geothermal energy and geological storage of CO2.

News in brief
Geoheritage and geodiversity accessible to all thanks to digital technology
Emerging in the 1990s, the notions of geoheritage and geodiversity have been receiving growing attention from academic communities, international organizations and public authorities. (...) It was in this context that, in 2020, IFPEN signed a partnership agreement with UNESCO, one of the objectives of which is to share digital tools facilitating the promotion of geoheritage and geodiversity to the general public...

News in brief
X-rays and Neutrons for imaging salt migration
Salt precipitation in permeable rocks is a risk faced by some energy sectors, particularly for gas storage in geological formations during operational phases (injection and extraction), when there is contact with saline aquifers. (...) This precipitation reduces the space where fluids can circulate, altering rock permeability, or even leading to plugging under certain conditions. In order to understand the underlying mechanisms behind this damaging phenomenon, experiments examining gas flow in a brine-saturated porous medium were conducted on IFPEN’s CAL-X flow test bench...

News in brief
Underground modeling: an essential step for the energy transition
To address the challenges of the energy transition, the subsurface has an important role to play, both in terms of providing resources and offering storage solutions. (...) Numerical models can help gain a better understanding of the subsurface with a view to its long-term management and optimal use. Developed for a number of years now at IFPEN, initially for the petroleum industry, such models cover scales ranging from the sedimentary basin to the reservoir...

News in brief
Global change, impact on landscapes and water resources
Today, the impact of climate change and human activities on the evolution of landscapes and water resources is a major challenge. Predicting it requires dedicated tools capable of evaluating, 100 years ahead, the consequences of different scenarios on watersheds and groundwater. To this end, IFPEN is developing modeling approaches targeting erosion-transport-deposition phenomena combined with surface and subsurface flows. ...